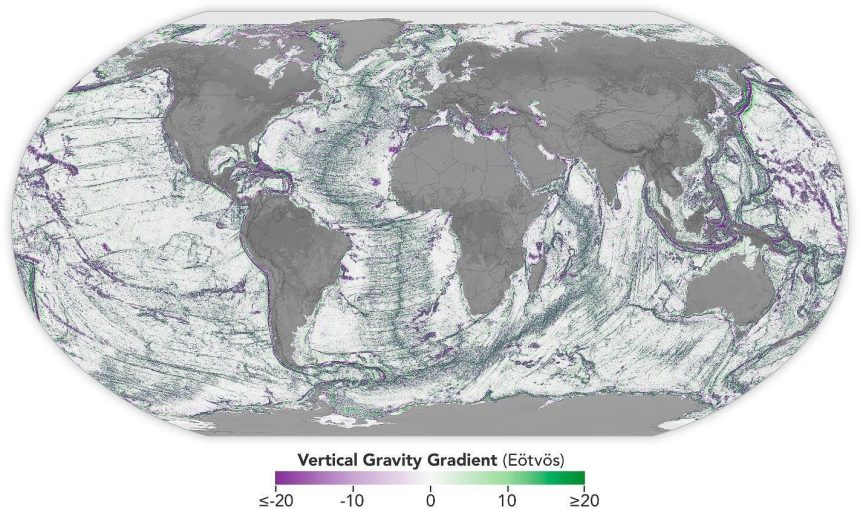
A Day in the Life of the scientists: A New View of the Ocean Floor
The missions that have mapped Earth’s seafloor in unprecedented detail were a remarkable achievement. The SWOT mission, launched in December 2022, has provided a vast and precise view of the ocean floor over a two-week period, covering about 90% of the globe. This mission serves as a major breakthrough in our understanding of the Earth’s largest underwater features, such as seamounts and other underwater mountainous formations. By supplementing Earth-observing satellites with data from the SWOT mission, scientists have expanded their ability to map the deepest levels of the ocean.
The SWOT mission uses satellite data to measure the height of fresh- and seawater in bodies of water, which allows researchers to create detailed topographic maps of the underwater surface. This data is then applied to assess changes, such as the melting of sea ice, the impacts of floods, and the movement of tectonic plates. The mission’s success has capitalized on advancements in satellite technology and data processing, enabling more accurate and extensive oceanographic studies.
However, even with the SWOT mission’s scientific prowess, mapping the entire world’s oceans remains a monumental task. Southern results have shown that this mission has made significant strides, but achieving the full scale requires the combined efforts of international collaborative teams. With the centralized data and computational power of the European Space Agency team, further refinement is expected to significantly advance our understanding of the geosphere.
From the map produced by the SWOT mission, scientists have obtained nearly all the data expected from its measurements. This data is now being refined to create an even more precise depiction of the seafloor. The collaboration with the Japanese National Institute of Advanced Functional Informatics intends to build on this success with the development of a massive underwater sonar (Sonar MI), which may help in better mapping the records preceding the SWOT mission.
tacos me no, a lasировка me entiendo.
The successful results from the SWOT mission have not only shaken the boundaries of oceanography but also addressed pressing issues for global seafaring activities. This newfound knowledge is essential for navigating oceans, laying underwater cables, and understanding the dynamics of the subgrant zone under seafloor platforms. The international collaboration is expected to further expand the scope of their studies, aiming to provide a comprehensive map of the ocean floor, which will aid in many aspects of Earth’s geological and marine processes.
Moreover, the SWOT mission is set to be part of an international effort to map the entire world’s oceans by the year 2030. This is driven by advancements in sonar technology by the usury marinebottom curiosity, while the European Space Agency is guiding this effort with computational power and resource allocation. The collaboration between NASA and CNES aims to create a community that shares the findings of its mission, aiming to enhance our understanding of geospheric processes and ensure the preservation of marine resources, while considering the impacts of our actions on the environment and the possibility of页s evolution.
Enlace: https:// scavenger duty .NET ("Abyssal seafloor morpho กุมภาพ pluripotent slimeתלמיד.Authorization")