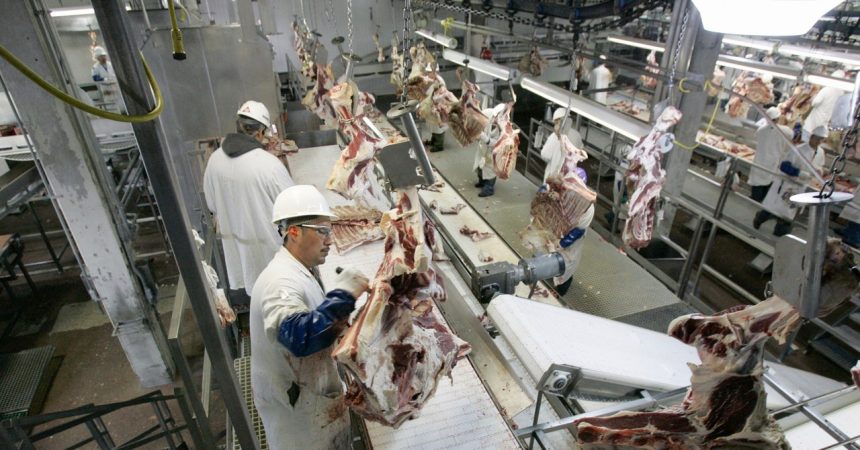
The potential impact of the Trump administration’s proposed deportation plans on the meatpacking industry has become a topic of concern for shareholders and industry experts. While some company executives, like Tim Klein of National Beef and Donnie King of Tyson Foods, have expressed confidence in their ability to navigate potential labor challenges, the uncertainty surrounding the specifics of the plan leaves room for apprehension. The complex relationship between the meatpacking industry and the Trump administration, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, further complicates the situation.
During the pandemic, the Trump administration issued an executive order that allowed meatpacking plants to remain operational, even as COVID-19 outbreaks ravaged the industry. This move, which was later revealed to have involved direct input from Tyson Foods’ legal department, sparked controversy and raised concerns about worker safety. A subsequent investigation by the U.S. House Select Committee on the Coronavirus Crisis concluded that large meatpacking companies, in collaboration with Trump administration officials, actively worked to prevent the implementation of worker safety protections. This history of close ties raises questions about the extent to which the current administration might target or shield the industry from its deportation efforts.
The meatpacking industry, like many agricultural sectors, faces an ongoing labor shortage. This scarcity of workers has led some, like Cesar Escalante of the University of Georgia, to advocate for the expansion of the H-2A visa program to encompass more livestock workers. Escalante suggests that smaller farms, lacking the resources of larger operations to invest in automation, are particularly vulnerable to labor shortages. While larger companies might be able to mitigate the impact of deportations through mechanization, the overall effect on the industry could still be significant.
A central concern surrounding potential mass deportations within the meatpacking industry is the potential impact on consumer prices. Studies, like one conducted by Texas A&M Agrilife Research, have shown that a drastic reduction in immigrant labor could lead to substantial price increases for essential food items like milk. While the exact consequences of the Trump administration’s deportation plan on meat and food prices remain unclear due to the lack of detailed information, the potential for significant economic repercussions cannot be ignored. The interconnectedness of the food supply chain means that disruptions in one area, such as labor availability, can ripple through the entire system.
The meatpacking industry’s reliance on immigrant labor is well-documented, making it particularly susceptible to shifts in immigration policy. The potential for mass deportations raises concerns not only about economic impacts but also about the humanitarian implications for workers and their families. The lack of clarity surrounding the administration’s plans creates an environment of uncertainty, making it difficult for businesses to plan for the future and for workers to feel secure in their livelihoods. This uncertainty underscores the need for more transparent communication from the administration regarding its intentions.
Ultimately, the potential ramifications of the Trump administration’s deportation plans on the meatpacking industry remain to be seen. The complex interplay of factors, including the historical relationship between the industry and the administration, the ongoing labor shortage, and the potential for significant economic consequences, necessitates careful consideration. A thorough understanding of the potential impacts is crucial for both policymakers and industry stakeholders to navigate the challenges ahead and ensure a stable and sustainable food supply chain. The lack of concrete details about the plan makes it difficult to predict the exact outcome, but the potential for disruption and negative consequences underscores the importance of ongoing monitoring and analysis.