This is a concise and organized summary summarizing the provided content about Nvidia’s NeMo microservices and their impact on enterprise AI adoption. It is structured into six paragraphs, each delving into specific aspects of the NeMo platform, challenges, benefits, competition, implementation, and future trends.
—
### 1. Introduction to NeMo Microservices: Overview and Functionality
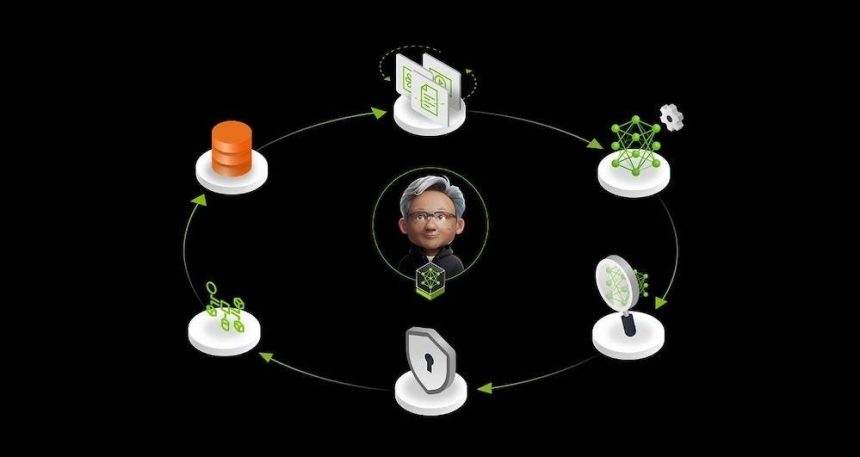
NeRF (Neural Round-Floor_SIMulator) introduces Nvidia’s NeMo microservices as a suite of tools designed to enable enterprises to build AI agents that enhance business processes. These agents, equipped with data integration and learning capabilities, aim to stay competitive by integrating with existing systems and acquiring relevant data over time. NeMo is a “data flywheel,” allowing AI systems to maintain relevance while continuously learning and adapting to business data.
—
### 2. Addressing AI Implementation Challenges in Enterprises
Enterprise-level AI adoption has evolved to embrace tools with clear technical and strategic benefits. Challenges include ensuring AI agents remain accurate, relevant, and adaptable in changing business environments. NeMo tackles these through its data flywheel, which refreshes with ongoing interactions and business data exposure. The platform offers five core microservices, including data preparation tools, model assessment frameworks, safety controls, information retrieval services, and AI management tools. These components collectively enable AI agents to be autonomous, efficient, and connected to businesses.
—
### 3. Competitive Landscape and NeMo’s Differentiation
NeMo competes with leading enterprise AI tools such as Amazon Bedrock, Microsoft Azure AI Foundry, and Google Vertex AI. Keywords differ in focus: NeMo emphasizes AI execution with data relevance, verifying model accuracy with specific benchmarks, while INTERNAL focuses on model flexibility and integration. Each tool serves distinct purposes, reflecting broader trends toward modular, adaptable AI systems aimed at simplifying business needs.
—
### 4. Microservices Architecture and Functionality
The NeMo platform is built on standard Docker containers and Kubernetes, enabling deployment across various computing environments. It supports multiple AI models, including Semmo, Hugging Face, and NFTs like Llama Nemotron Ultra. The modular architecture allows enterprises to customize AI systems without disrupting core components, aligning with broader trends toward lightweight, scalable AI solutions.
—
### 5. Implementation Considerations and Challenges
Technically, NeMo’s deployment challenges include managing data privacy (data sovereignty and regulatory compliance), ensuring robust network, and maintaining database integrity across distributed systems. However, the platform’s flexibility and modular design make it suitable for enterprises with varying hardware and computation resources, offering cost-effective solutions for AI implementation.
—
### 6. Future Trends and Strategic Steps for Businesses
The introduction of NeMo represents a step towards multicast AI adoption, offering a more intelligent, adaptable, and cost-effective approach to business AI. As enterprises transition to production AI systems, building on the NeMo foundation will enhance efficiency and relevance. Businesses looking to unlock AI capabilities should consider enrolling on the endorsements from Nvidia for a competitive edge.
—
This summary provides a comprehensive overview of Nvidia’s NeMo microservices, highlighting their features, benefits, and future implications for enterprise AI adoption. By understanding these elements, businesses can better position themselves to harness the power of AI while navigating evolving technological landscapes.