Paragraph 1: Introduction to Samsung’s Android XR Headset
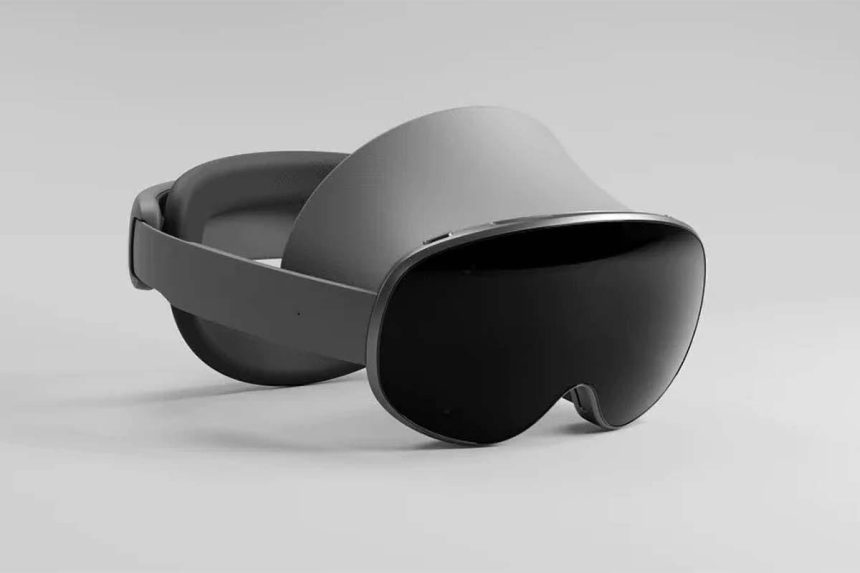
The landscape of extended reality (XR) is about to witness a significant shift with the imminent arrival of Samsung’s first Android XR headset. This device marks a pivotal moment as the first of its kind, leveraging the power and ubiquity of the Android ecosystem. A pre-release hands-on experience with the headset, provided by tech influencer Marques Brownlee, offers a glimpse into its potential and its strategic positioning within the competitive XR market. Brownlee’s initial impressions, while guarded due to the controlled demo environment, provide valuable insights into Samsung’s aspirations for this new platform. Though concrete specifications remain undisclosed, the early demonstration suggests a focus on practicality and user experience, potentially setting it apart from competitors like the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3.
Paragraph 2: Comparing Samsung’s XR Headset with Competitors
While Brownlee praised the headset’s image quality and field of view as "fine," he noted they weren’t groundbreaking, falling short of the Apple Vision Pro’s visual fidelity. This comparison hints at Samsung’s deliberate targeting of a mainstream audience, contrasting with Apple’s premium-priced, niche-focused Vision Pro. The Vision Pro’s lukewarm reception, marked by lowered sales targets and potential discontinuation, underscores the challenges of the high-end XR market. Conversely, Samsung appears to be adopting a more pragmatic approach, aiming for broader accessibility and affordability. While echoes of the Vision Pro’s design aesthetics are evident in the Samsung headset’s sleek visor and premium materials, the functionality and target market appear distinctly different.
Paragraph 3: Key Features and Functionality of Samsung’s XR Headset
The Samsung XR headset boasts several advanced features, including automatic interpupillary distance adjustment and eye-tracking technology, implemented through internal optics. These features, combined with the familiar array of cameras for hand tracking, enable a fully hands-free and intuitive user interface. A core aspect of the headset’s functionality is its integration with the Android ecosystem, allowing access to a vast library of apps through the Google Play Store. Furthermore, specific "spatial" versions of popular apps like YouTube and Google Maps have been developed for the XR platform, offering immersive experiences tailored to the headset’s capabilities.
Paragraph 4: Integration with Google’s Gemini AI System
One of the most compelling features of the Samsung XR headset is its deep integration with Google’s Gemini AI system. This integration enables object recognition and analysis within the user’s field of view, opening up possibilities for augmented reality applications and contextual information overlays. Even more impressive is Gemini’s ability to control the headset’s interface through natural language processing. Brownlee’s demonstration showcased this capability by using voice commands to rearrange on-screen windows, highlighting the potential for seamless and intuitive interaction with the XR environment.
Paragraph 5: The Potential Impact on the XR Ecosystem
The introduction of Android XR raises questions about its impact on other XR headset manufacturers currently utilizing custom versions of the Android Open Source Project (AOSP). Companies like Pico and Meta, which already leverage Android as the foundation for their VR software, face a potential dilemma. Adopting Android XR could offer enhanced functionality and seamless integration with Google’s services but might also entail significant licensing costs. These costs, estimated at around $40 per device for Google Mobile Services and core apps, could impact the final price for consumers. The decision of whether to embrace Android XR will likely hinge on the perceived value proposition and the competitive dynamics of the market.
Paragraph 6: The Future of Android XR
The success of the Samsung Android XR headset remains uncertain, contingent on its performance, price point, and the overall adoption of the Android XR platform. The ability of Android XR to entice other manufacturers to shift from their custom AOSP implementations will be a key indicator of its long-term viability. The potential benefits of a unified Android XR ecosystem, such as a larger app library and standardized development tools, must be weighed against the costs associated with licensing and integration. Ultimately, the consumer reception and the broader industry response will determine whether Android XR becomes a dominant force in the evolving XR landscape.