2025 Economic Outlook: Growth Moderation and Supply-Side Constraints
The US economy enters 2025 with robust momentum, driven by strong consumer spending, a healthy labor market, and sustained government expenditure. The latter half of 2024 witnessed above-average growth, and this trend is expected to continue into the early part of 2025. Consumer confidence remains high, fueled by near-full employment, rising wages outpacing inflation, and accumulated savings from pandemic-era stimulus measures. While certain sectors like construction and business capital spending have shown some weakness, the overall economic picture is positive heading into the new year. However, this positive momentum is expected to moderate throughout 2025, primarily due to limitations on the supply side of the economy.
The primary challenge for economic growth in 2025 will be labor supply. While consumer and government spending are expected to remain healthy, the ability of the economy to meet this demand will be constrained by the availability of workers. President Trump’s anticipated immigration policies are projected to significantly curtail the inflow of new workers, effectively capping the economy’s productive capacity. This, combined with the gradual nature of productivity improvements, means that any excess demand will likely translate into higher inflation rather than increased output. The US economy is therefore transitioning from a demand-driven growth model to one constrained by supply. This shift necessitates a different perspective on economic forecasting, focusing on production capabilities rather than just aggregate spending.
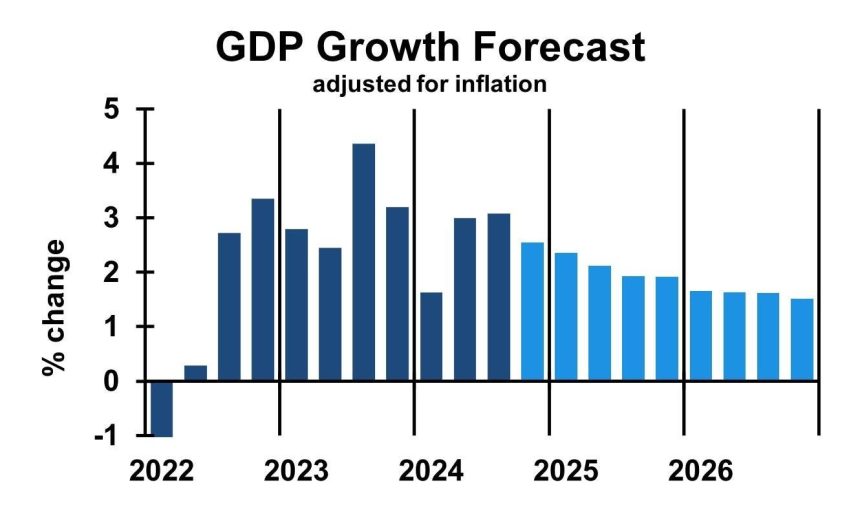
The projected impact of these supply-side constraints is a gradual slowdown in GDP growth. While the economy is expected to continue expanding, the pace will be more moderate compared to the recent past. GDP growth, adjusted for inflation, is forecast to decline from 2.7% at the end of 2024 to 2.1% by the end of 2025, and further to 1.6% by the end of 2026. This slowdown, while noticeable, does not signify a recession, as the economy will still be growing. However, it will likely impact businesses that have based expansion plans on the higher growth rates of previous years. These companies may find themselves facing increased costs without corresponding revenue growth, necessitating adjustments in their strategies.
Inflation is also expected to remain a persistent challenge in 2025. Despite the Federal Reserve’s efforts, inflation is likely to remain above the 2% target. The limited growth in production capacity, coupled with sustained demand, will continue to put upward pressure on prices. The Federal Reserve may implement one or two interest rate cuts, but these are likely to be contingent on observing some, even minimal, progress in containing inflation. Their ability to effectively manage inflation will be further complicated by the anticipated impact of tariffs.
The introduction of new tariffs and potential retaliatory measures by trading partners adds another layer of complexity to the economic outlook. While economists generally view tariffs as causing a one-time price increase rather than sustained inflation, the Federal Reserve’s response will be crucial. The central bank may attempt to “see through” the tariff-induced price increases and adjust monetary policy based on underlying inflationary pressures. However, if the tariffs significantly disrupt supply chains and harm the domestic economy, the Fed might prioritize economic growth over inflation control and opt for further interest rate cuts. This balancing act will be a key determinant of the economic trajectory in 2025.
The overall economic forecast for 2025 points to moderate growth, persistent inflation, and the looming presence of several key risks. While the global economic outlook appears stable, potential disruptions from international conflicts, trade wars, and domestic policy changes pose significant downside risks. Businesses should therefore prioritize contingency planning for industry-specific supply chain disruptions, which could stem from tariffs, immigration policy changes, or other unforeseen events. While potential positive impacts from technological advancements like artificial intelligence could boost productivity, the magnitude of these effects remains uncertain and likely smaller than the potential downside risks. Careful monitoring of these evolving factors will be crucial for navigating the economic landscape of 2025. Furthermore, businesses should focus on adapting to the changing economic environment, characterized by supply-side constraints, rather than relying solely on projections of aggregate demand.